Soil Monitoring with IoT uses technology to empower farmers and producers to maximise yield, reduce disease and optimise resources. IoT sensors can measure soil temperature, NPK, volumetric water content, photosynthetic radiation, soil water potential and soil oxygen levels. Data from the IoT sensors are then transmitted back to a central point (or the cloud) for analysis, visualisation and trend analysis.
The resultant data can then be used to optimise farming operations, identify trends and make subtle adjustments to conditions to maximise crop yield and quality. The use of IoT in agriculture is known as Smart Agriculture (or Smart Farming), and IoT is a central component of Precision Farming.
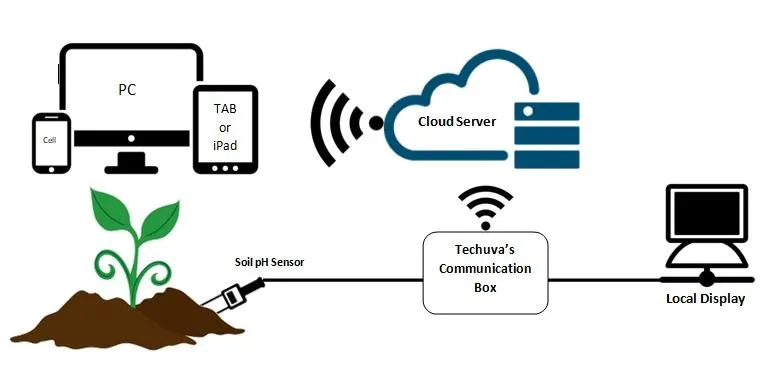
What can I measure with Smart Agriculture / IoT sensors?
Smart Agriculture is focused on soil, weather and crop conditions. Given the importance of weather and irrigation, many Smart Farming solutions are coupled with Smart Environment (Air Quality) and Smart Water (Pollution, Turbidity, Nutrients) for a complete solution. The most common IoT sensors are listed below:
Soil Temperature
Soil temperature is an essential factor in belowground plant activity, influencing root growth, respiration, decomposition and mineralisation of nitrogen. IoT sensors can estimate soil temperature by measuring air temperature and other factors; however, the most accurate measurement is to use a probe buried in the soil.
Depending on the root structure of the plant in question, multiple probes can be installed at different depths. Surface soil temperature can be monitored using a different type of IoT sensor that uses IR technology.
- Soil temperature.
- Non-Contact surface temperature.
Soil Moisture
The moisture content of soil can also be monitored using buried probes with electrodes. In hydrology, soil science and agricultural moisture content play a vital role in soil chemistry, plant growth and groundwater recharge. Soil moisture content is essential for several reasons:
- Water in the soil serves as a critical nutrient for all crops and plants.
- Water is an essential component of photosynthesis.
- Crop yield is heavily influenced by the availability of water in the soil.
- Soil water is an important carrier of soluble food nutrients for plant growth.
- Soil water helps regulate soil temperatures.
Soil science is a complex area, and suffices to say; that it is beyond the scope of this article! IoT and Smart Agriculture technology from Libelium can measure the following:
- Soil moisture (3 x depths)
- Conductivity.
- Volumetric water content.
- Soil water potential.
Solar Radiation
IoT sensors can measure different types of solar radiation that play a vital role in photosynthesis. Beyond basic light levels of Lux, IoT can measure the following:
- Solar – Photosynthetically active radiation.
- Solar – UV.
- Solar – Shortwave.
Solar radiation can have a real impact on plant-growth, and IoT enables you to monitor solar levels to understand correlations and trends.
Weather
Rainfall/precipitation, wind, humidity and atmospheric pressure all play an essential role in plant growth. Our Smart Agriculture systems support several advanced weather stations. Weather stations and soil sensors give you a 360 view of your farming operation. IoT weather stations can measure the following:
- Precipitation (optical and tipping bucket measurements).
- Temperature.
- Humidity.
- Air pressure.
- Wind speed.
- Wind direction.
Soil sensors
Nitrogen, Phosphorous and Potassium (pot-ash) sensors are relatively new to the market but provide a method in which these key soil nutrients can be measured using IoT sensors. NPK IoT sensors use various technologies, but TDR is a common method used by these sensors. NPK sensors support RS485 to be integrated into IoT solutions, including LoRaWAN and data loggers.
Combined sensors can measure:
- Nitrogen
- Phosphorous
- Potassium
- pH
- EC
- Temperature
- Moisture
NOTE: NPK sensors are in a development phase and the accuracy/sensitivity of these sensors does vary between vendors. MTG is helping trial on some next-generation NPK sensors that will hopefully lead to the increased accuracy of these sensors.
Other Measurements
We support many other IoT sensors for agriculture and are valuable in specific niche scenarios. Although not soil monitoring, they enhance any IoT deployment. These additional sensors include:
- Vapour pressure
- Soil oxygen levels.
- Leaf and flow-bud temperature.
- Leaf wetness.
- Trunk, stem and fruit diameter.
Wireless Communications for IoT and Smart Agriculture
A key benefit of IoT solutions is the wide range of wireless communication options available. IoT is not just limited to urban areas with extensive mobile coverage; support for LoRaWAN, 4G, Zigbee, Sigfox, WIFI and Satellite mean Smart Farming/Agriculture solutions work find in both urban, rural and very-remote environments. IoT systems’ low-power nature means nodes and sensors can be powered by battery, solar or other renewable sources.
How can I use the data?
The effective use of data and insights really depends on your environment and application.
- Web-based dashboards can visualise data.
- Mobile apps and mobile optimised web pages can visualise data for mobile devices.
- Data can be imported or accessed using analytical tools such as Excel, PowerBI or Tableau.
- Dashboard and monitoring systems can generate alerts if thresholds are exceeded (i.e. NPK levels, soil moisture, etc.)

